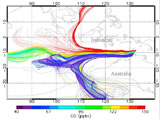
Researchers have discovered a “chemical equator” in Asia where higher levels of pollution from the Northern Hemisphere are prevented from mixing with largely uncontaminated air from the Southern Hemisphere. Scientists have long known that air from the two hemispheres tended not to mix, but previously thought that a belt of low pressure, the Intertropical Convergence Zone, formed the primary barrier. But new air sampling by University of York researchers has found a 30-mile-wide barrier well north of the Intertropical Convergence Zone. The chart below illustrates the barrier, with relatively pure air — shown in violet — circulating from the Southern and Indian oceans and meeting the polluted air, shown in red and yellow, flowing from the north. Levels of carbon monoxide are four times higher north of the barrier, in part because of forest fires in Sumatra and Thailand. Formation of the “chemical equator” is due to a combination of oceanic and atmospheric conditions and its discovery should help researchers better track the movement of global pollutants.
Study Finds `Chemical Equator’Separating Pollutants From Hemispheres
More From E360
-
WATER
After Ruining a Treasured Water Resource, Iran Is Drying Up
-
FILM
At a Marine Field Station, Rising Seas Force an Inevitable Retreat
-
Energy
To Feed Data Centers, Pennsylvania Faces a New Fracking Surge
-
SPACE
Scientists Warn of Emissions Risks from the Surge in Satellites
-
WILDLIFE
A Troubling Rise in the Grisly Trade of a Spectacular African Bird
-
MINING
In Myanmar, Illicit Rare Earth Mining Is Taking a Heavy Toll
-
INTERVIEW
How Batteries, Not Natural Gas, Can Power the Data Center Boom
-
ANALYSIS
As U.S. and E.U. Retreat on Climate, China Takes the Leadership Role
-
Solutions
From Ruins to Reuse: How Ukrainians Are Repurposing War Waste
-
ANALYSIS
Carbon Offsets Are Failing. Can a New Plan Save the Rainforests?
-
Energy
Facing a Hostile Administration, U.S. Offshore Wind Is in Retreat
-
Biodiversity
As Jaguars Recover, Will the Border Wall Block Their U.S. Return?