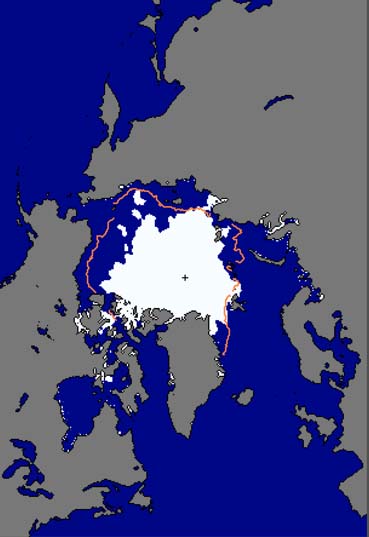
The Arctic Ocean’s rapidly disappearing cover of summer sea ice has shrunk to the second lowest level on record and may reach a record minimum extent by the time the melt season ends next month, according to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). The image at left shows sea ice cover, in white, as of August 26, with the orange line indicating the average sea ice cover for that day from 1979 to 2000; this year’s ice extent is 760,000 square miles smaller than the historical average, meaning the ice has shrunk by an area nearly three times as large as Texas. Arctic sea ice now covers 2 million square miles. The record low, set last September, was 1.65 million square miles, and NSIDC scientists say that record could be broken next month if this summer’s melting trends continue.
Arctic Sea Ice Nears Record Low
More From E360
-
Energy
To Feed Data Centers, Pennsylvania Faces a New Fracking Boom
-
SPACE
Scientists Warn of Emissions Risks from the Surge in Satellites
-
WILDLIFE
A Troubling Rise in the Grisly Trade of a Spectacular African Bird
-
MINING
In Myanmar, Illicit Rare Earth Mining Is Taking a Heavy Toll
-
INTERVIEW
How Batteries, Not Natural Gas, Can Power the Data Center Boom
-
ANALYSIS
As U.S. and E.U. Retreat on Climate, China Takes the Leadership Role
-
Solutions
From Ruins to Reuse: How Ukrainians Are Repurposing War Waste
-
ANALYSIS
Carbon Offsets Are Failing. Can a New Plan Save the Rainforests?
-
Energy
Facing a Hostile Administration, U.S. Offshore Wind Is in Retreat
-
Biodiversity
As Jaguars Recover, Will the Border Wall Block Their U.S. Return?
-
WATER
An E.U. Plan to Slash Micropollutants in Wastewater Is Under Attack
-
INTERVIEW
This Data Scientist Sees Progress in the Climate Change Fight