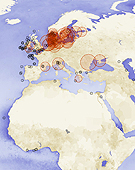
A new NASA map illustrates the significant expansion of the world’s marine dead zones, deepwater regions where dissolved oxygen is so low marine species cannot survive. Many of these dead zones occur off densely populated coastlines, particularly along the eastern United States and in Northern Europe. Scientists produced the map using data from satellites that can detect high concentrations of particulate matter, an indicator of overly fertile waters that can create dead zones. The zones arise when fertilizers applied to crops wash into streams and rivers, eventually reaching coastal waters, where the excess nutrients trigger massive algae blooms. When the algae die, they sink to the ocean’s depths, where they essentially become fertilizer for microbes that decompose the organic matter and consume oxygen, suffocating marine life. In 2008, a study found that dead zones had spread exponentially since the 1960s, affecting more than 400 ecosystems and a total area of more than 152,000 square miles (245,000 square kilometers).
Map Illustrates Extent of the Planet’s Marine Dead Zones
More From E360
-
WILDLIFE
A Troubling Rise in the Grisly Trade of a Spectacular African Bird
-
MINING
In Myanmar, Illicit Rare Earth Mining Is Taking a Heavy Toll
-
INTERVIEW
How Batteries, Not Natural Gas, Can Power the Data Center Boom
-
ANALYSIS
As U.S. and E.U. Retreat on Climate, China Takes the Leadership Role
-
Solutions
From Ruins to Reuse: How Ukrainians Are Repurposing War Waste
-
ANALYSIS
Carbon Offsets Are Failing. Can a New Plan Save the Rainforests?
-
Energy
Facing a Hostile Administration, U.S. Offshore Wind Is in Retreat
-
Biodiversity
As Jaguars Recover, Will the Border Wall Block Their U.S. Return?
-
WATER
An E.U. Plan to Slash Micropollutants in Wastewater Is Under Attack
-
INTERVIEW
This Data Scientist Sees Progress in the Climate Change Fight
-
Climate
As Floods Worsen, Pakistan Is the Epicenter of Climate Change
-
Climate
Heat Stress Is a Major Driver of India’s Kidney Disease Epidemic